Composites for green defense - a project with Censec
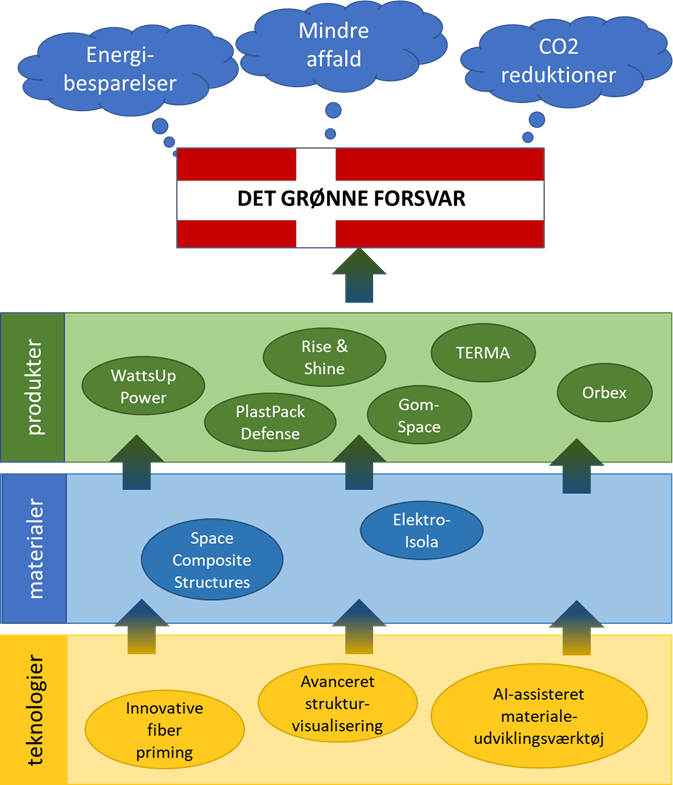
The Danish Defense's Green Action Plan 2021-2025 outlines the direction for reducing waste and CO2 production within the Danish military.
Composite materials are used in a variety of applications within the military as well as in the broader society. These materials are highly sought after, primarily due to their strength and lightness. However, the production of many composite materials is energy-intensive, as it often requires high temperatures and pressures. Moreover, there is typically significant consumption of, for example, solvents. A large percentage of the material ends up as waste after cutting, and at the end of their life cycle, it is currently impractical to recycle composites due to the high costs and energy requirements.
Industrial collaboration with the Danish Technological Institute and Censec
In the project "Composites for Green Defense", we are working with a consortium of Danish composite manufacturers to explore how the use of composite materials and improvements in the production chain can result in a smaller climate and environmental footprint. We are investigating the potential of utilizing machine learning to design new composites with specialized properties. At the same time, we employ advanced characterization methods to better understand the composition and fracture points of specific composite materials.
Project Activities
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for predicting optimal composite compositions: In collaboration with two foreign technology companies, workshops are being held to deepen our understanding of how AI can learn from established and newly developed research. These tools can predict the properties of a composite material, significantly reducing the time- and cost-intensive process associated with developing and testing new materials.
X-ray synchrotron analysis of composite components: As part of the project, X-ray tomography measurements were conducted at the ESRF synchrotron in Grenoble. These non-destructive measurements provide deep insights into the materials. The results offer quantitative data on, for example, the quantity and size of porosities, internal fractures, and the orientation of individual fibers and fiber bundles. This analysis helps our partners better understand their materials, whether immediately after production, after testing, or following environmental exposure.
Data visualization of fiber composites: In collaboration with the Alexandra Institute, 3D visualization tools are being developed to enable navigation through the layers of the material. These tools allow for the separation of, for example, fibers and the matrix, providing insights into the homogeneity and distribution of subcomponents within the material.